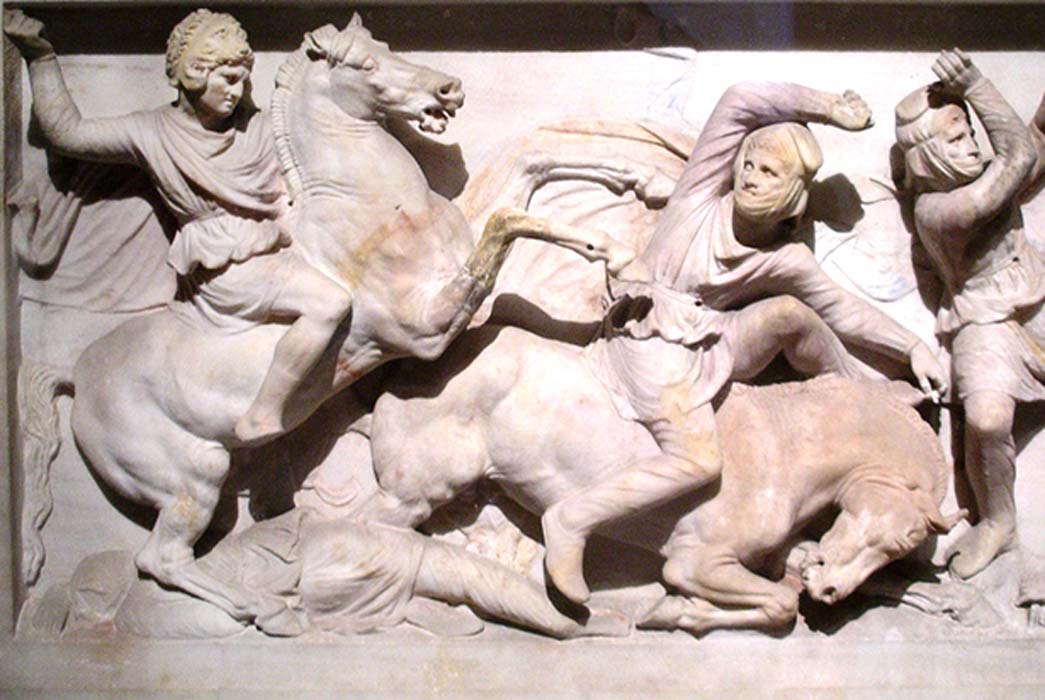
Alexander the Great Destroyer? The Sacking of Persepolis and The Business of War – Part I
Alexander the Great has gained an immortality in his strong presence in our minds as well as in the history books. Known for a greatness of military genius and diplomatic skills, he conquered most of the known world of his time and brought on a new era of the Hellenistic World. But who really was Alexander, the man?
The intention of this article is not to go into the whole history of Alexander’s invasion and conquest of the Near East, but rather to look at the man himself. In doing so, we will understand why Alexander invaded and will dispel some of the myths about Alexander’s intentions, in turn helping us to understand why the Greco-Macedonian Empire broke apart a little over a hundred years after his death. Nearly all traces of his once glorious empire had been tossed into the ash heap of history.
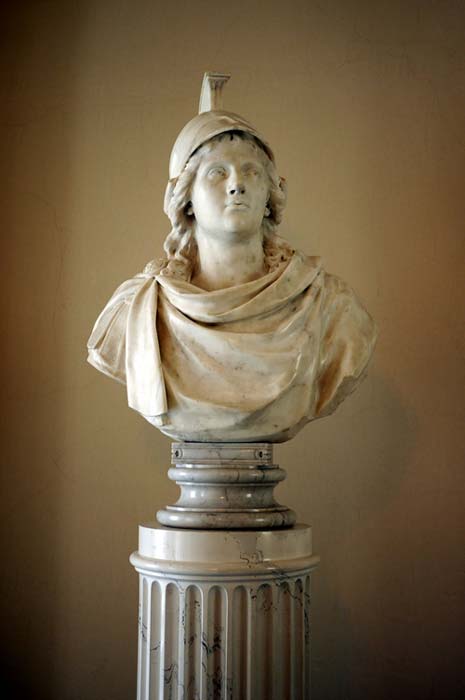

A bust of Alexander the Great (CC BY-ND 2.0)
The War Business
The army that King Philip II of Macedon left to his son Alexander was semi-professional and a paid fighting force. In order for Alexander to pay for this army, either he had to disband a portion of it to save money, risking much in doing so, or he had to go on the march to save his kingdom. Alexander choose to save his kingdom at another empire’s expense. Alexander needed to pay the bills, but would do so by looting Persia.
He proved what Randolph Bourne once stated; “War is the health of the state.” Alexander was the state, and war was his business. Therefore, revenge was the excuse to avoid personal monetary debt. Besides Alexander’s dilemma in possibly going into debt within a matter of weeks, he also had a rather large personal ego to contend with as well.
Upbringing and Education
Alexander’s ego is said to have been rather massive. His mother had huge expectations for him and led him to believe that he would conquer Persia. If you think about it, the only huge deed at the time in proving one’s destiny was to conquer Persia, for it was the biggest challenge at the time in the known world, at least in the Greco-Macedonian sense. Besides being hounded about his destiny, he also was a competitor from birth, as he would try to outdo his father in combat, being more aggressive in battle and showing absolute courage in the face of danger just to win Papa’s approval. Alexander worried that nothing would be left to achieve beyond the successes of his father, Philip.
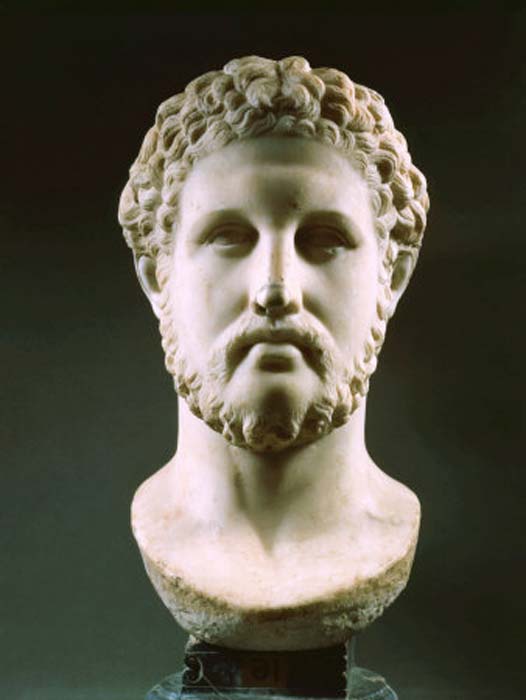

Bust of Philip II of Macedon, a 1st-century Roman-era copy of a Greek original. (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Besides his home life, Alexander was enthralled by the epic poems of Homer and his detailed journeys into war and individual heroism. These themes fueled the young Alexander’s imagination as he grew, along with the help of his tutor, Aristotle. The works of Homer instilled the romantic rebels of the Greek legends, such as Achilles or even Hercules—who Alexander modeled himself after and who he claimed to be descended from—while Aristotle provided the reasoning in Alexander’s curriculum. Alexander’s father, Philip, taught him war.