Bloody Hunts and War Games of the Armies of Khan: The Mongol Military – Part II
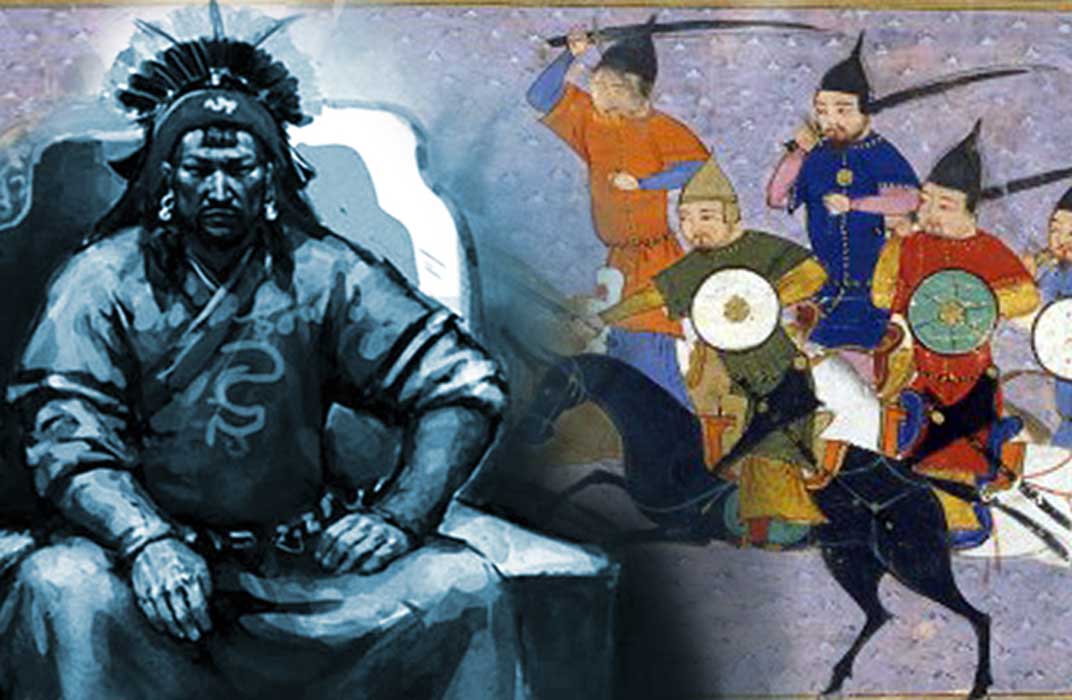
Genghis Khan, founder and emperor of the Mongol Empire rarely needs an introduction, but it is crucial in understanding how he gained his place in history by examining the Mongol military organization he pieced together to become one the world’s greatest fighting machines ever seen. How did he do it?
Military Organization
Mongol military organization based on decimal lines under Genghis Khan was nothing new. Other steppe peoples, like the Khitan and Jurched had been using the same system for many years beforehand. Genghis Khan was introduced to this military system during his time with Ong Khan. The system introduced by Genghis Khan to the Mongols was structured as arban, jagun, minqan, and tumen.
Mongol military leadership started with the arban at the bottom of the chain. Every Mongol warrior belonged to an arban. An arban consisted of 10 men with one being the commander. Ten arbans equaled one jagun (plural jaghut) consisting of 100 men. Ten jagunt consisted of 1000 men and formed a minqan (plural minqat). Ten minqat formed one tumen (plural tumet) consisting of 10,000 men.
10 men = 1 arban
100 men = 1 jagun
1000 men = 1 minqan
10000 men = 1 tumen
100000 men = 1 Tuc
The military organizational structure was divided into three corps that consisted of the baraghun ghar (right flank), je’un ghar (left flank), and tob or gol (center or pivot). To move this large army the command structure of course started with the Great Khan, who issued orders to three commanders in charge of the three tumen. See the figure below.