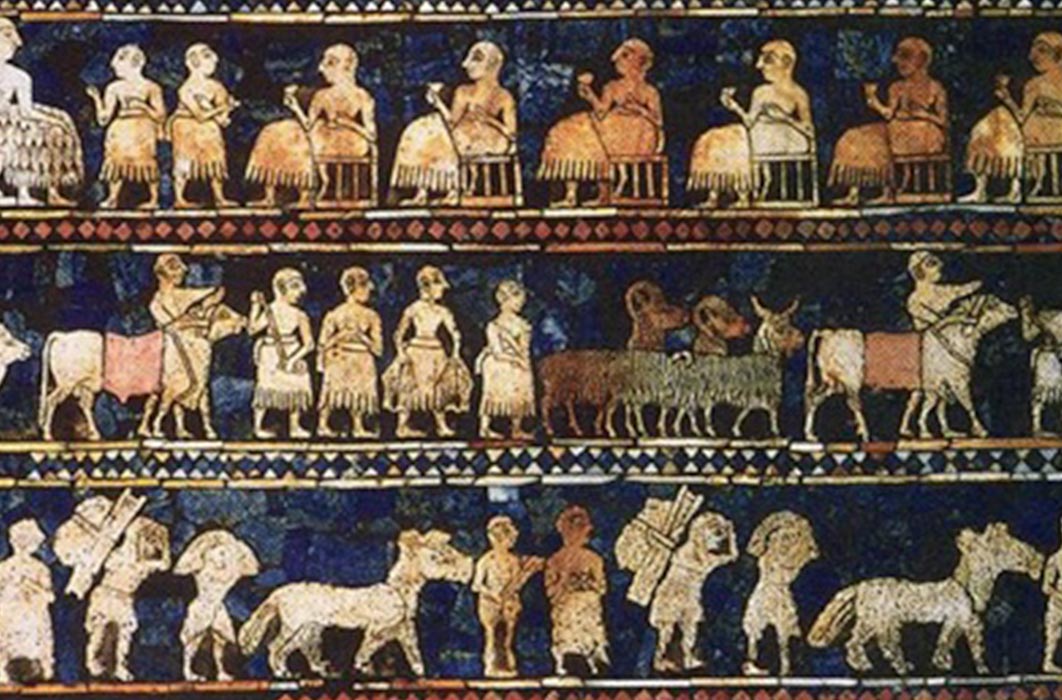
Changing History: The Ferris Wheel of Lost Civilizations
Although history textbooks often present information as if it is set in stone and firmly established, recent research into ancient civilization reveals one embarrassing fact that continuously seems to elude expert analysis. Simply put, no one culture ever claims to be the first. Civilizations which have formed and, in some cases, disappeared, almost always seem to come equipped with a back story. In virtually every historical example, someone came before. No matter how far back in time one goes, legends and mythologies of founders who had mysteriously arrived from somewhere else rise to the surface.
Tel Moza
Take, for example a recent discovery announced by the Israel Antiquities Authority in July of 2019. It put the dating of the whole traditional Agricultural Revolution hypothesis into question. Archaeologists uncovered evidence of a city at Tel Moza, that seemed to exist in a transforming phase between hunting/gathering culture and the invention of agriculture, casting doubts upon traditional theories of urban life in the Levant.
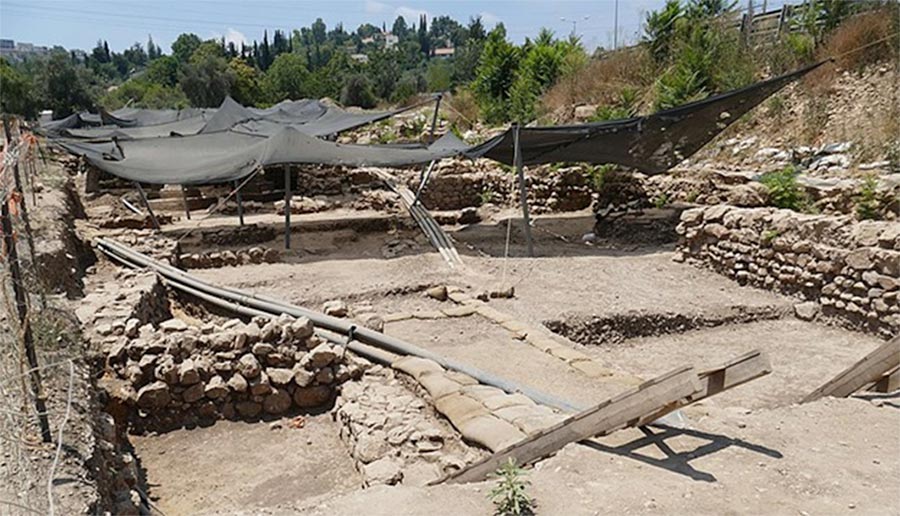

Archaeological excavations near Motza, Israel. (Bukvoet / CC BY-SA 4.0)
While engaged in a highway construction project, Israeli workers brought this previously undiscovered and unknown city that supported a population of 2,000 to 3,000 people, to light. A group of archaeologists led by Dr. Hamoudi Khalaily and Dr. Jacob Vardi worked on the project for 18 months. What they revealed was a huge stone age settlement about a third of a mile (half a kilometer) in length. It contained residential buildings, places of worship, alleyways, and plastered floors and walls. Back in its heyday it would have been considered metropolis, producing indications that people had lived in this fertile valley for perhaps as long as 20,000 years.
As of yet there has been no official apology in the popular press confirming that so-called ‘alternative historians’ may have been correct in their assessments of ancient origins, but these and other discoveries forces one to believe that no one really knows where and when civilization began.
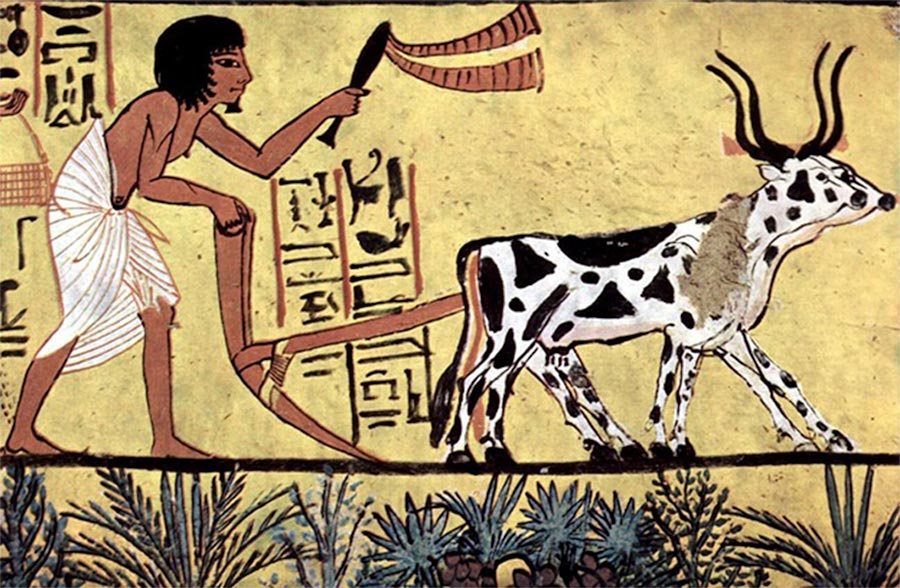

Ancient agriculture. Mural in the burial chamber of Sennedjem (circa 1200) (Public Domain)
What is Civilization?
There is a baseline that most archaeologists accept, but before describing it some definitions are in order. What, for instance, is meant by the word ‘civilization’? Most theories assume that civilization began with settled towns or cities. A ‘civilized’ culture is thus an urban one. This, of course, requires a stable food supply, which eliminates any cultures that existed before the Agricultural Revolution. So, by definition, ‘civilization" could not have started before the Neolithic era that began, at the earliest, some 12,000 years ago. Most textbooks, especially those published before the discovery of Turkey's Göbekli Tepe, place it closer to 6,000 BC. Since evidence of a written record begins in the Middle East, one winds up with a relatively late date and narrow geographical location. Accepted rubrics put ‘civilized’ man in Mesopotamia or Egypt some 6,000 years ago, although this position is crumbling very quickly.
A stable food supply makes it possible to develop specialized labor. That is what creates imposing buildings, works of art, skilled warfare, organized religion, trade, writing, a recorded history, and a centralized bureaucracy to run things. But not all civilizations employ all of those skills. The inhabitants of Peru, for instance, seem to have got along fine without a written language. But generally speaking, civilizations are said to come into existence when the mainstays fall into place.