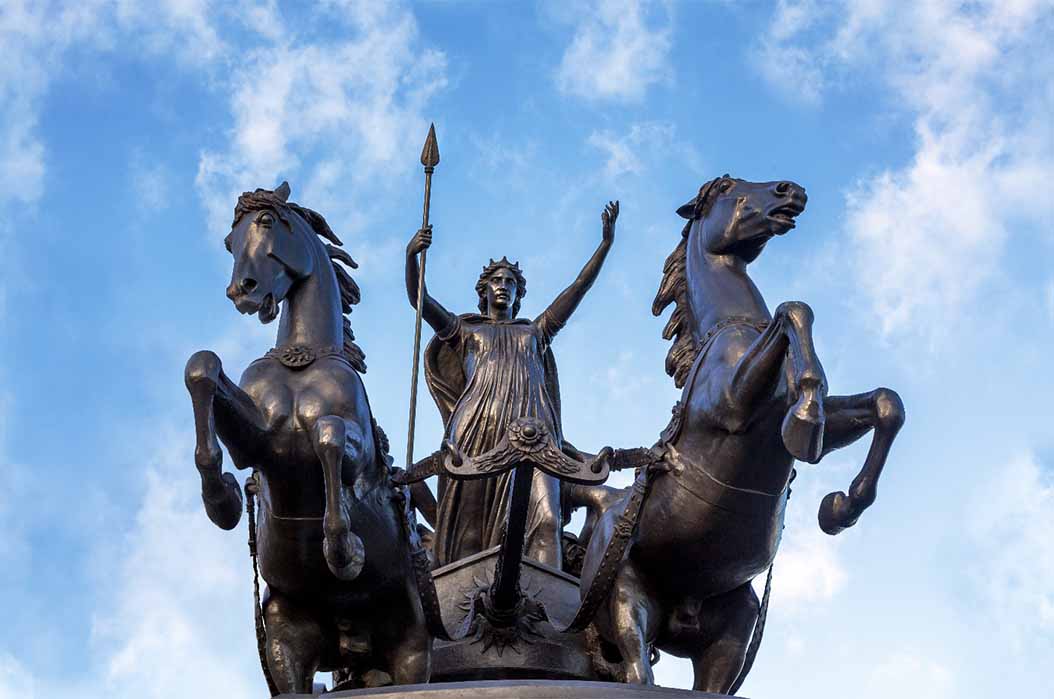
Venta Icenorum: Excavating Romans In Boudicca’s Lands
Today the sleepy village of Caistor St Edmund in the country of Norfolk with its typical church spire and green, seems unremarkable but 2,000 years ago the terrain helped shaped the future of the whole of Britain. Just outside the village lies the ruins of Venta Icenorum, a Roman town whose name means the ‘marketplace of the Iceni’.’ The name was preserved in a third-century Roman document called the Antonine Itinerary, and Venta Icenorum was the site of a Roman settlement built at the heart of Iceni lands. The Iceni were an Iron Age tribe who meteorically rose to fame under their Queen Boudicca in 60-61 AD when they fought the might of invading Rome, badly bloodying her nose, before being killed en masse in a final desperate battle.
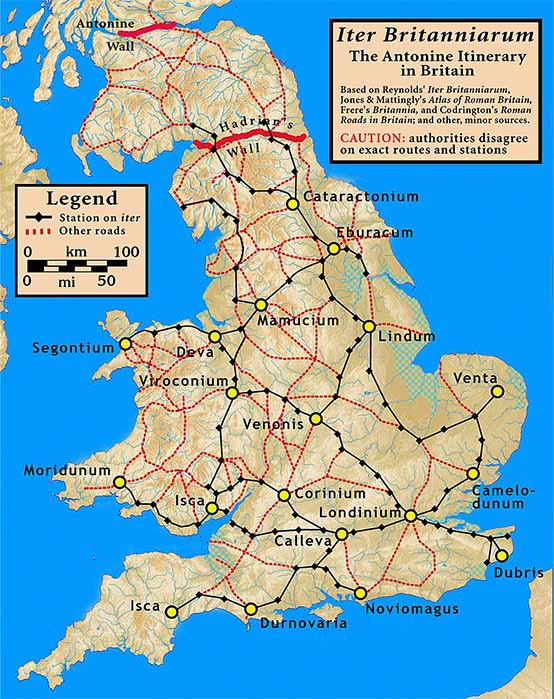
Main Roman cities and roads in Roman Britain, according to the "Antonine Itinerary" (CC BY-SA 3.0)
Boudicca’s Revolt
Boudicca's Revolt is one of Britain's most enduring historical stories and quickly became legend, and she was and remains a vivid symbol of British resistance against invading tyranny. Boudicca possibly began life as a Brigantian, but at some point she married the Iceni King Prasutagus. The Iceni ruled what is now the East Anglian county of Norfolk, and parts of Cambridgeshire, Suffolk and Lincolnshire. This was a marshy fenland, poor for growing crops so the Iceni focused their attention on metalwork and horsemanship, producing the earliest known British coins.

Iceni coins from Norfolk (The Portable Antiquities Scheme/ CC BY-SA 2.0)
The Iceni briefly revolted when the Romans first arrived on British shores in 47 AD but ultimately they became a client kingdom, permitted to remain largely independent provided they acknowledged Roman overlordship and paid tribute. All seemed well, until King Prasutagus died in 60 AD. He and Boudicca had two daughters and in an attempt to protect them from Roman threats upon his death, he appointed the Emperor Nero heir to the Iceni lands alongside his daughters in his will. Rome, never one to accept women holding positions of power, ignored the will, declared Iceni lands part of the Roman province of Britannia and sent the procurator Catus Decianus to receive their submission. He ordered that Boudicca be flogged, her daughters raped and called in all Roman loans.

Boudicca Haranguing The Britons by John Opie, R.A. (1761-1807) (Public Domain)
Outraged, Boudicca and the Iceni, along with Trinovantian allies, revolted. The Roman historian Tacitus puts in her mouth a famous speech whereby she declares that “I am avenging my scourged body, the outraged chastity of my daughters….this is woman’s resolve; as for men they may live and be slaves if they will.”