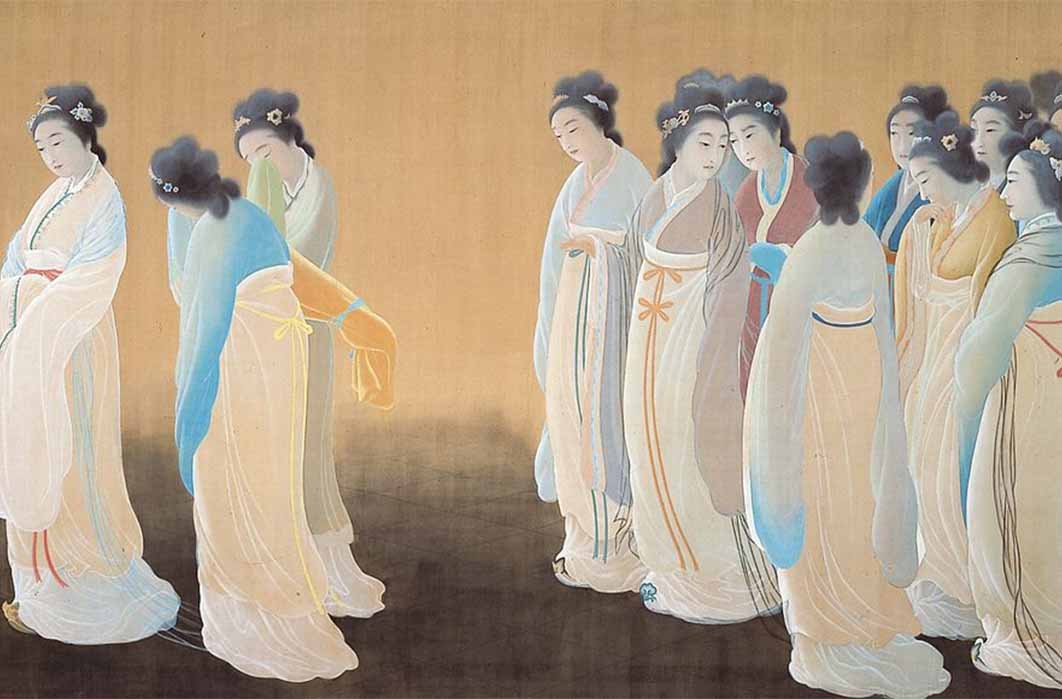
The Currency Of Chinese Princesses In Conjugal Peace Alliances
For thousands of years, the institution of marriage has been in a constant state of evolution. The established form of marriage recognized in each country, religious or social group at any given time is often colored with slight, but interesting variations. One can easily imagine scholars and historians at times throwing up their hands in frustration when people refer to ‘traditional marriage’ as there are far too many traditions, cultures, and time periods to consider. Marriage contracts and ceremonies were first documented in Mesopotamia in approximately 2350 BC, and the Bible tells that King Solomon had 700 wives and 300 concubines.
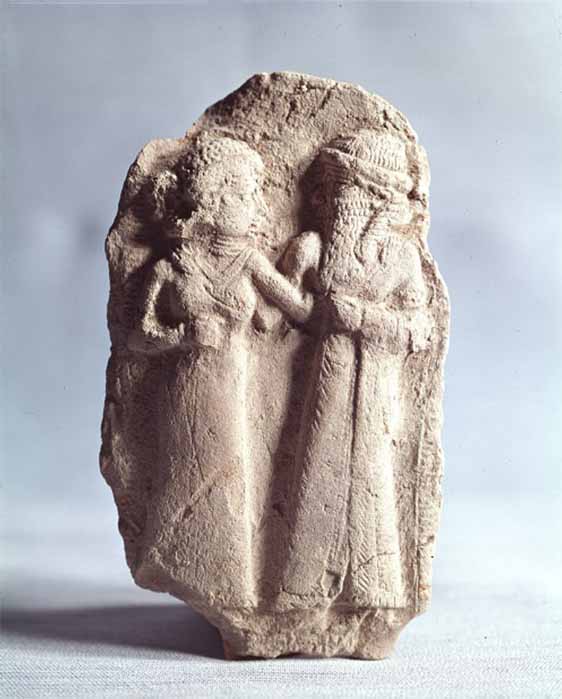

The marriage between the Sumerian gods Inanna and Dumuzid ( Françoise Foliot/ CC BY-SA 4.0)
Families whose bloodline is important to power or inheritance would often regard marriage as a more political, non-romantic formality in which a potential spouse is considered not only for their virtue and appearance, but also for their wealth and power. These are referred to as dynastic marriages where a careful selection of a spouse is required to sustain a family's royal status. Consideration would include the size of the land governed or controlled by the family as well as the stability of control over that territory, for when there is territorial instability within royal realms, other royals are less likely to marry into that family as it would weaken their own position. Another factor to consider is the royal families' political alliances. A marriage could secure an alliance between two dynasties that sought to reduce their perception of threat from other dynasties. This could also improve a dynasty's chances of acquiring territory by obtaining legal claim to a foreign throne, or portions of its realm, through inheritance from an heiress if a monarch had no male heir.
The Legendary Peace-Making Marriage Of Helen Of Sparta
The contest for the hand and subsequent marriage of Helen, princess of ancient Sparta in Greece, may be one of the most well-known tales in mythology, which tells of the necessity of surrendering a female member of a ruling family to gain peace or shore up alliances between city-states ruled by oligarchies or acknowledged royalty. When Helen of Sparta reached marriageable age, kings and princes came to court her, as she was renowned for her beauty. Some sent emissaries with extravagant gifts for Helen and her family, and others personally delivered these gifts. Menelaus, who later won Helen's hand in marriage, did not attend, but was represented by his brother King Agamemnon of Mycenae.
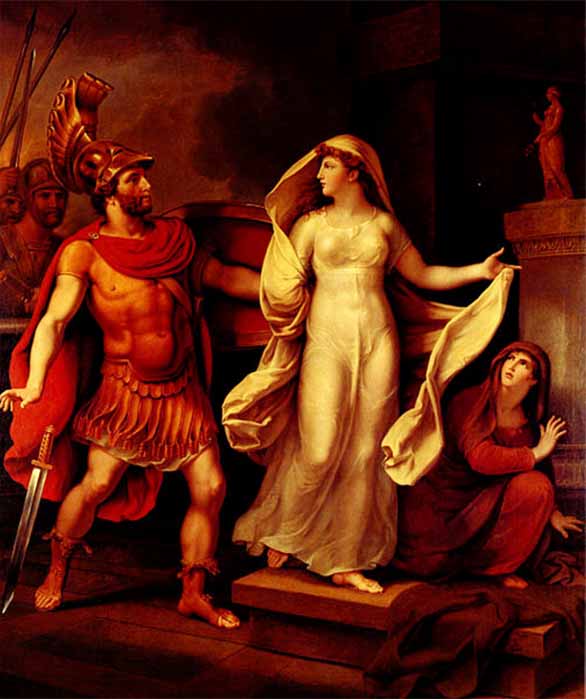

Helen and Menelaus by Johann Heinrich Wilhelm Tischbein (1816) (Public Domain)
With so many powerful and potentially competitive rivals vying for Helen's hand, their host, King Tyndareus, Helen's father, feared that choosing a husband would alienate the rest of suitors and cause hostilities. Odysseus, king of Ithica did not even bother to bring a gift as he knew he had no chance of winning Helen's hand. Odysseus proposed a solution in exchange for Tyndareus' support in his courtship of Penelope, the daughter of Icarius, Tyndareus' brother. When Tyndareus agreed to this arrangement, Odysseus proposed that before the husband was chosen, all of Helen's suitors should swear an oath to defend the chosen husband against whomever opposes him. Thus, the suitors were oath-bound to protect Helen and her husband, whomever he may be. Menelaus was chosen as Helen's husband after all the suitors had sworn this pact. After the marriage, Menelaus, Helen and by extension her family – including Agamemnon - benefitted from the oaths taken by her suitors, every one of whom were powerful kings and warriors in their own rights. Thus, they were all honor-bound to unite when Helen was taken by Paris, prince of Troy.
Powerful Marriage-Alliances in Ancient Egypt
For the upper classes in the ancient world, marriage also served as a means of preserving power, with kings and other members of the ruling class marrying off their daughters for a number or reasons such as to end wars, form alliances, acquire land and produce legitimate heirs to rule their kingdoms after them. The Egyptian-Hittite peace treaty in 1259 BC, the world's oldest known surviving peace treaty, was sealed by the marriage of Pharaoh Ramesses II and a Hittite princess Maathorneferure, daughter of King Hattusili III and his wife, Queen Pudu-Kheba.