A Pharaoh’s Exploits Recorded for All Time: The Battle of Megiddo—Part I
With the death of the famous female Pharaoh – Hatshepsut – Thutmose III rose to power and knew there would be trouble. On the banks of the Orontes River, a revolt was brewing. Amassing a huge army and heading out on a forced march, the Egyptian king prepared for battle.
The Battle of Megido pitted the Egyptians, led by Pharaoh Thutmose III on one side, against a coalition of Canaanites led by the King of Kadesh. Megiddo is a battle of firsts, such as a recorded body count and the first use of the composite bow. Moreover, Megiddo is considered the first recorded battle due to the reliable detail provided by the Egyptians. Details of the battle come from the 42 year of Thutmose’s reign, as he instructed his scribe, Tjaneni, to keep a daily journal, in order to have his military exploits, particularly the 14 campaigns that took place in the Levant (Canaan), inscribed by his artisans on the walls of Amun-Re's temple at Karnak.
The Battle of Megiddo is regarded to have taken place 16 April 1457 BCE.
A Battle for Position and Goods
Power-shifts taking place in the strategic location— on the Great Bend of the Eurphates River north of Egypt— was the beginning of the conflict. The Asiatic kingdom that Thutmose was concerned about was the city-state of Kadesh on the Orontes River, which was under the protection of the Kingdom of Mitanni.
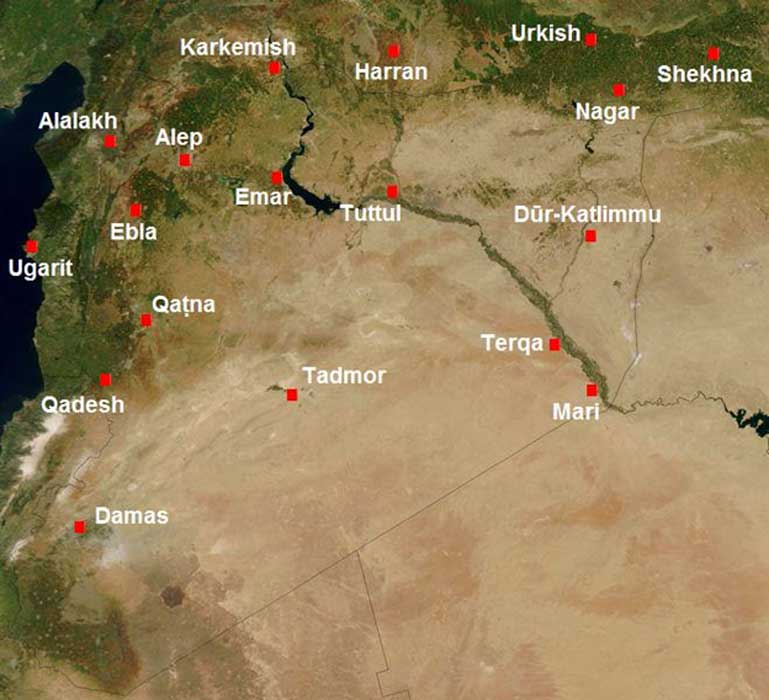
Main cities of Syria in the second millennium BCE. Kadesh, or Qadesh, is to the west. (Public Domain)
This protection allowed Kadesh to expand southward into Canaan and to confiscate many of the mini-states and expand its influence as far south as the city of Megiddo. Kadesh understood the geographical strategic importance of Megiddo, for whoever controls the city effectively controlled the Esdraelon Plain in Galilee. More important was that Megiddo controlled the main trade routes that flowed east into the Trans-Jordan as well as to the north leading to the city-state of Kadesh. If Kadesh, along with their protectorate, Mitanni, controlled the trade routes leading east and north, it also would affect the trade flowing from Egypt to the south. Therefore, Egypt could not fully partake in the lucrative trade flowing from the rich lands of Mesopotamia. As 19th century French Liberal economist Frederic Bastiat was to have said, “When goods don't cross borders, soldiers will.” It seems evident that goods did not cross or if they did, they were next to none.
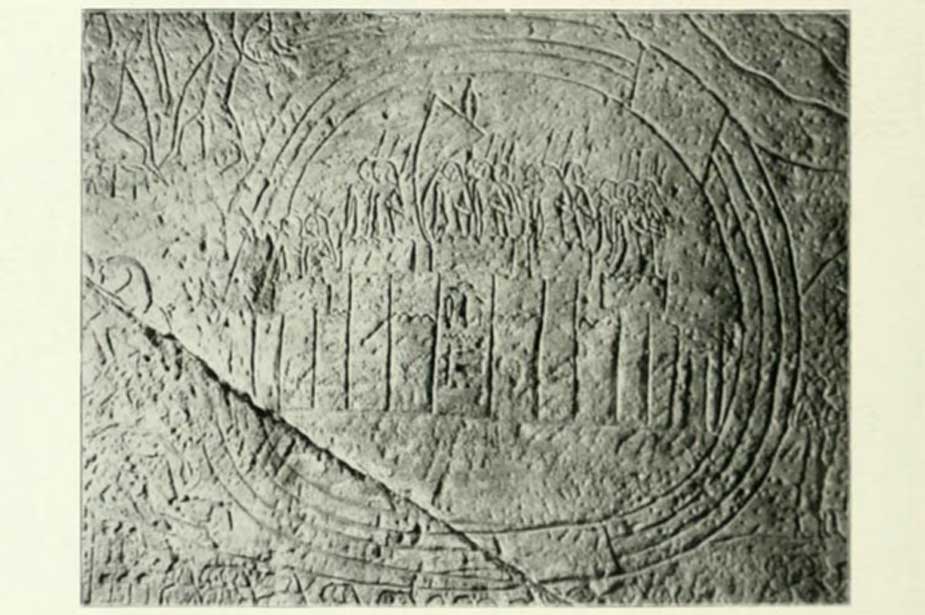

Egyptian relief depicting Kadesh garrisoned by Hittites and surrounded by the Orontes River, Reign of Ramesses II, 19th dynasty. (Public Domain)