Women in Power in Ancient Times
The narrative of history often celebrates male rulers, warriors, and thinkers, yet the annals of ancient times are also adorned with the tales of formidable women who wielded significant power and influence. These women, from queens and pharaohs to priestesses and warriors, left indelible marks on their societies and shaped the course of history. Exploring the pages of history and the thrilling lives of these powerful women, as well as their achievements, the challenges they faced, and the legacies they left behind is truly an eye-opening journey. By examining historical records, archaeological findings, and scholarly interpretations, we can gain a nuanced understanding of the roles and impacts of these remarkable women in ancient civilizations.
Ancient Egypt: The Reign of Female Pharaohs
Ancient Egypt stands out as a civilization where women could attain the highest levels of power. The most notable examples are the female pharaohs, who not only ruled as sovereigns but also undertook significant military, architectural, and religious endeavors.
1. Hatshepsut
Hatshepsut (c. 1507–1458 BC) is one of the most prominent female pharaohs of ancient Egypt. Ascending to the throne as regent for her stepson Thutmose III, Hatshepsut eventually declared herself pharaoh. Her reign, marked by peace and prosperity, saw extensive building projects, including her famous mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahri. Hatshepsut portrayed herself in the traditional iconography of a male king, complete with a false beard, to assert her legitimacy. Her trade expeditions, notably to the Land of Punt, brought wealth and exotic goods to Egypt, further cementing her legacy as a powerful and effective ruler.
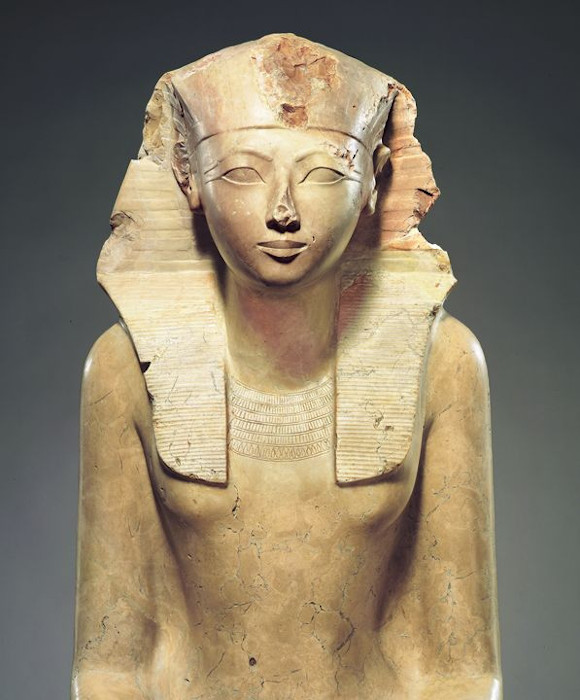

Seated statue of Hatshepsut. (Metropolitan Museum of Art / CC BY-SA 1.0)
2. Cleopatra VII
Cleopatra VII (69–30 BC) is arguably the most famous female ruler of ancient Egypt. Known for her intelligence, political acumen, and romantic liaisons with Julius Caesar and Mark Antony, Cleopatra's reign was marked by her efforts to preserve Egypt's independence amid the expanding Roman Empire. Cleopatra was a shrewd diplomat and a strategic thinker, using her relationships to forge political alliances. Her dramatic suicide following the defeat by Octavian's forces ended the Ptolemaic dynasty and marked the beginning of Egypt as a Roman province.
- The Three Husbands of Fulvia, the Leading Lady of the Ancient Roman Elites
- 4 Powerful and Inspiring Women Rulers that Changed Society and the World
3. Hetepheres I
Hetepheres I, the mother of Pharaoh Khufu, played a crucial role in the early dynastic period of ancient Egypt. Living during the Fourth Dynasty (c. 2600 BC), Hetepheres I was the wife of Sneferu, the founder of the dynasty, and was deeply revered as the queen mother. Her influence is evident from the lavish grave goods discovered in her tomb, which included jewelry, furniture, and other artifacts. These items, now invaluable to archaeologists, underscore her significant status and the respect she commanded in Egyptian society. The discovery of her intact tomb provided invaluable insights into the burial practices and material culture of the Old Kingdom, highlighting the reverence afforded to royal women in ancient Egypt.
Mesopotamia: Priestesses and Queens
In Mesopotamia, women held various significant positions, particularly in religious and political spheres. The roles of priestesses and queens in ancient Sumer and Akkad demonstrate the influence women wielded in these early civilizations.